Get in touch.
Questions about our services or looking to partner up?
Drop us a message we look forward to connecting.
Executive Summary:
Agentic AI represents the next evolution of artificial intelligence systems—autonomous, goal-driven agents capable of planning, reasoning, taking actions across systems, and continuously learning from outcomes. Unlike traditional AI models that respond to prompts or predefined workflows, agentic AI systems orchestrate tools, APIs, data sources, and other agents to achieve complex business objectives with minimal human intervention.
As enterprises evaluate agentic AI adoption, a critical architectural decision arises: Should agentic AI be deployed on-premises or in the cloud? This white paper provides a structured, vendor-neutral analysis of both deployment models, examining architectural implications, security and compliance considerations, scalability, cost, governance, and real-world use cases. The goal is to help technology leaders make informed decisions aligned with business strategy, regulatory constraints, and operational maturity.
Understanding Agentic AI
What Is Agentic AI?
Agentic AI refers to AI systems designed around autonomous agents that can:
These agents often combine:
How Agentic AI Differs from Traditional AI
| Traditional AI | Agentic AI |
| Reactive | Proactive and goal-driven |
| Single-step inference | Multi-step reasoning and execution |
| Human-in-the-loop for most actions | Human-on-the-loop governance |
| Isolated use cases | End-to-end process orchestration |
Common Enterprise Use Cases
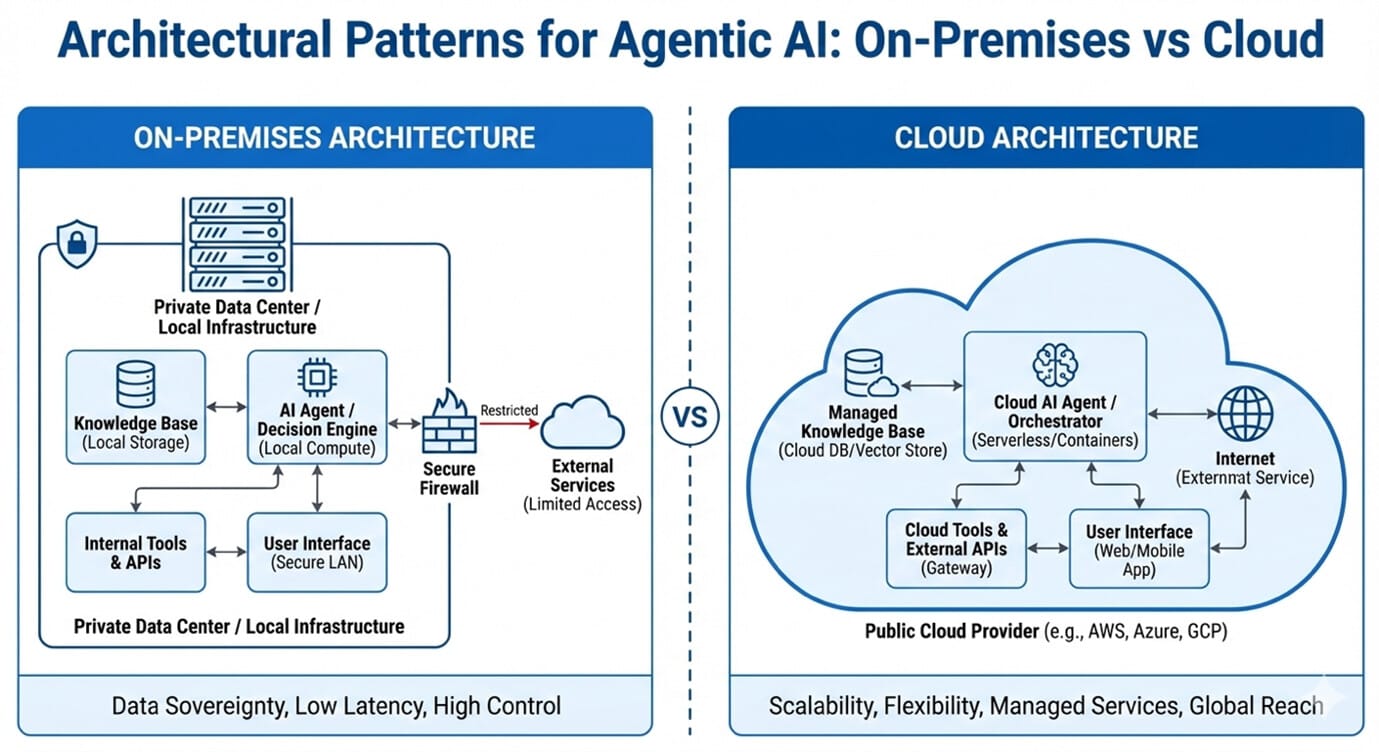
Deployment Models Overview
On-Premises Deployment Model
On-premises agentic AI is hosted entirely within an organization’s data centers or private infrastructure. This includes compute, storage, networking, AI models, orchestration layers, and integrations.
Typical Characteristics:
Cloud Deployment Model
Cloud-based agentic AI is deployed using public or private cloud platforms, leveraging managed AI services, scalable infrastructure, and cloud-native integrations.
Typical Characteristics:
Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Patterns
Many enterprises adopt hybrid approaches:
Security, Privacy, and Compliance
On-Premises: Security Advantages
On-Premises: Security Challenges
Cloud: Security Advantages
Cloud: Security Challenges
Compliance Considerations
Key compliance questions to address:
Performance, Scalability, and Cost
Performance
On-Premises:
Cloud:
Scalability
| Aspect | On-Premises | Cloud |
| Compute scaling | Hardware-bound | Elastic and near-instant |
| Agent concurrency | Limited | Massive |
| Experimentation | Slow | Rapid |
Cost Model Comparison
On-Premises:
Cloud:
Cost Optimization Strategies
Governance, Observability, and Control
Governance Requirements for Agentic AI
Agentic AI introduces unique governance challenges:
On-Premises Governance Strengths
Cloud Governance Strengths
Key Governance Capabilities
Observability Metrics
Decision Framework and Recommendations
When to Choose On-Premises
When to Choose Cloud
Hybrid as the Strategic Middle Ground
Hybrid deployments often provide the best balance:
Future Outlook
Agentic AI will increasingly:
Enterprises that invest early in a flexible deployment strategy—balancing control, scalability, and governance—will be best positioned to harness the full potential of agentic AI.
Conclusion
Choosing between on-premises and cloud deployment for agentic AI is not a binary decision. It is a strategic architectural choice shaped by regulatory context, risk appetite, operational maturity, and long-term AI vision. By understanding the trade-offs and adopting a principled decision framework, organizations can deploy agentic AI responsibly, securely, and at scale.