Get in touch.
Questions about our services or looking to partner up?
Drop us a message we look forward to connecting.
The transition from “AI curiosity” to “AI-driven business” is the defining challenge of 2026. While the previous 24 months saw a surge in experimental use cases, many organizations have hit a ceiling. The complexity of moving from a single-user prompt to an enterprise-grade agentic workflow involves more than just selecting the right Large Language Model (LLM).
This white paper provides a comprehensive technical and strategic framework for scaling AI. We examine the architecture of the “AI-First” enterprise, the evolution of the data stack, and the governance structures necessary to mitigate risk while maximizing ROI.
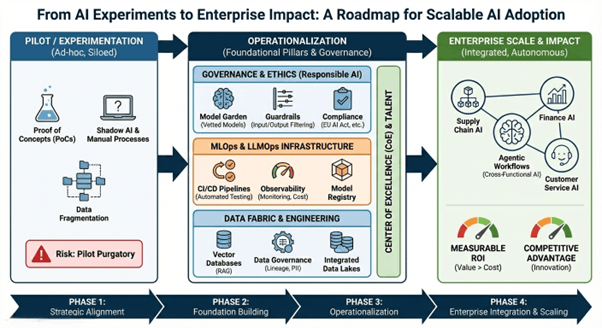
The State of the Market: Beyond Pilot Purgatory
As of early 2026, the industry has shifted from Model-Centric AI (focusing on the largest parameters) to System-Centric AI (focusing on how models interact with data and business logic). Organizations that fail to scale often suffer from “Pilot Purgatory”—a state where prototypes perform well in controlled environments but fail under the weight of real-world data drift, security requirements, and cost constraints.
The Scaling Gap
The Enterprise AI Reference Architecture
To scale, organizations must move away from “wrapper” apps and toward a modular architecture.2 The following diagram illustrates the modern stack required for enterprise impact:
The Infrastructure Layer (Compute & Orchestration)
Modern scaling requires a hybrid cloud approach. Enterprises are increasingly utilizing Sovereign Clouds for sensitive data and Burst Capacity for high-load training or fine-tuning sessions.
The Intelligence Layer (Model Router)
Rather than committing to a single model, leaders use a Model Router. This logic layer directs queries to the most cost-effective model based on complexity:
Data Strategy: The Bedrock of AI Impact
Data is no longer just “fuel”; it is the “moat.” A scalable roadmap requires a shift from static data warehouses to an active Data Fabric.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) vs. Fine-Tuning
The industry has reached a consensus: RAG is the preferred method for providing models with enterprise context, while Fine-Tuning is reserved for specific style or task-based optimization.
The Vector Evolution
Scaling AI requires high-performance vector databases that support Hybrid Search (combining semantic search with traditional keyword search).
LLMOps: Engineering Excellence for AI
If DevOps is about code, and MLOps is about data, LLMOps is about the lifecycle of the prompt and the model response.
The CI/CD Pipeline for AI
Traditional software testing isn’t enough. Scalable AI requires:
Cost Modeling and Unit Economics
Enterprises must calculate the Cost Per Successful Task (CPST) rather than just token costs.
Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC)
Scaling AI creates a massive surface area for risk. A robust roadmap includes a Responsible AI Framework that is baked into the code, not just written in a policy document.
| Risk Category | Mitigation Strategy | Technical Implementation |
| Hallucination | Truthfulness Benchmarking | RAG with citation verification. |
| Data Leakage4 | PII Masking5 | Automated redaction in the data ingestion pipeline.6 |
| Bias | Algorithmic Auditing | Multi-adversarial testing during red-teaming. |
| Shadow AI | Centralized API Management | OAuth2 integration for all LLM gateways. |
The 2026 Roadmap: A 12-Month Execution Plan
Scaling is a marathon, not a sprint. We recommend a phased approach:
Phase 1: Foundation (Months 1–3)
Phase 2: Operationalization (Months 4–7)
Phase 3: Expansion & Agentic Workflows (Months 8–12)
Financial Impact: Quantifying the Shift
ROI in 2026 is no longer just about “hours saved.” It is about Revenue Acceleration and Operational Resilience.
The Productivity Multiplier
By automating the “toil” of knowledge work, organizations are seeing a shift in the labor-to-output ratio
Recent benchmarks show that enterprises following this roadmap achieve a 35% reduction in operational overhead within 18 months of full-scale adoption.
Conclusion: The Mandate for 2026
The window for experimentation is closing. The competitive advantage now belongs to organizations that can bridge the gap between a successful lab demo and a resilient, governed, and cost-effective production system. Scalable AI adoption is not a technology purchase—it is an architectural and cultural evolution.